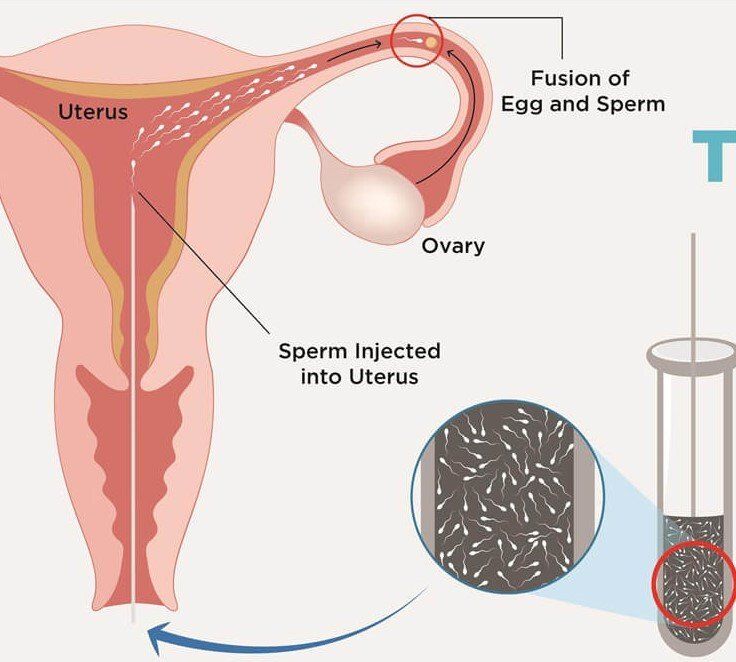
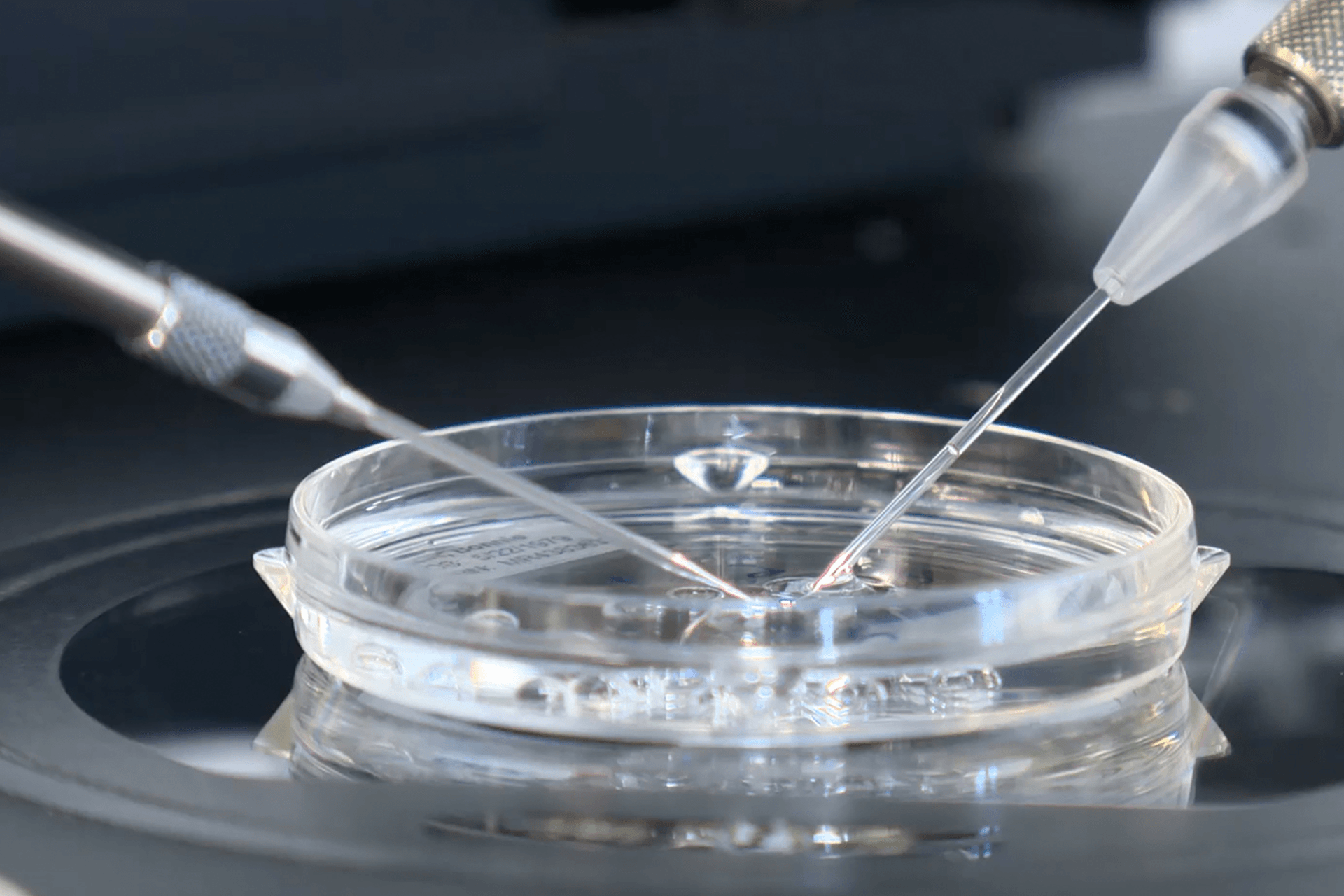
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is the most common advanced and widely accepted assisted reproductive technology (ART) treatment that has helped thousands of couples grow their families since it was first successfully performed in 1978. The procedure involves removing eggs from a woman’s ovaries and fertilizing them in an embryology lab with fresh or frozen sperm (from a partner or donor). The resulting embryos are cultured and transferred back into the uterus to achieve pregnancy.
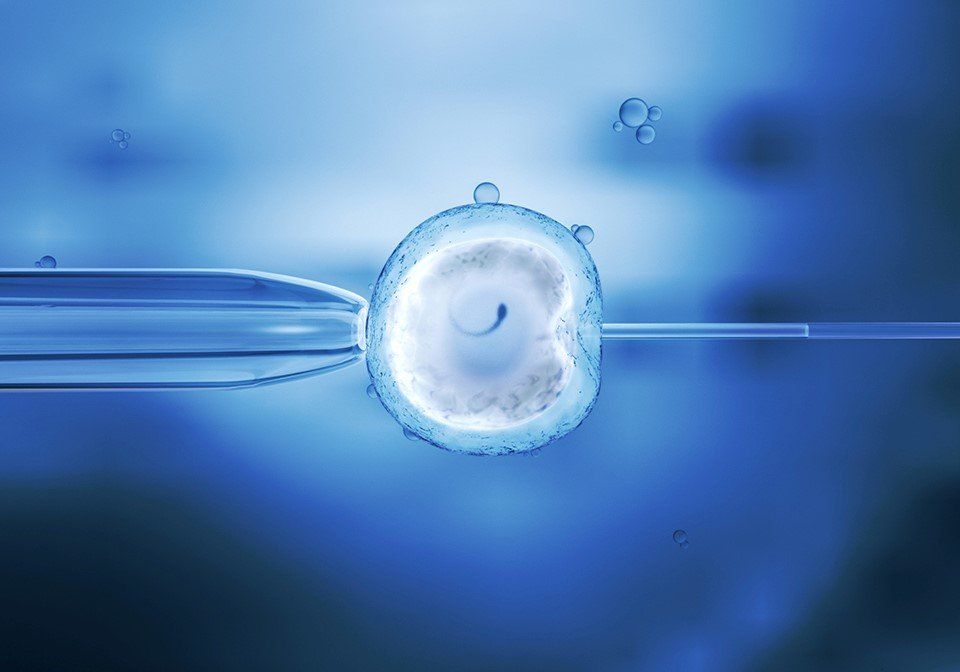
Common Indications for IVF Treatment
Once your diagnostic testing is complete, we will review your treatment options. Many patients are surprised to learn that IVF is not their only treatment option. However, IVF can be either the only or the most effective fertility treatment if you have :
- Tubal issues (blocked, damaged)
- Tubal removal or sterilization
- Male factor infertility (impacting sperm quality or quantity)
- Genetic disorders
- Unexplained infertility, Ovulation issues when IUI was not successful
- Fertility preservation
- LGBTQ+ family building
- Single parent
What is IVF
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a widely used fertility treatment that helps individuals and couples conceive when natural conception is challenging. The process involves retrieving eggs from the ovaries and fertilizing them with sperm in a controlled laboratory environment. The resulting embryos are then carefully transferred to the uterus to establish a successful pregnancy.
IVF is a safe and effective option for a variety of fertility challenges, including:
- Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
- Low sperm count or motility issues
- Endometriosis
- Unexplained infertility
- Age-related fertility decline
IVF at Precision IVF
At Precision IVF, whenever feasible, we start with basic, "low-tech" treatments like IUI and then transition to IVF when cheaper and less invasive treatment options are not successful. Studies show that after three to four treatment cycles, success rates with IUI begin to decline sharply. By moving to IVF treatment we are increasing your chances of success. Our cutting-edge IVF treatment protocols and customized treatment plans are designed to give you the best chances of achieving your dream family. Dr. Arya, as well as every member of our experienced team at Precision IVF and associated lab, is personally invested in your success. We take pride in providing affordable care in a compassionate environment and we would be honored to be a part of your journey.
Why Choose Precision IVF?
Choosing where to begin your fertility journey is an important decision. Here’s why patients trust Precision IVF:
- Experienced IVF specialists led by Dr. Arya.
- Personalized care plans tailored to your specific needs.
- Advanced lab technology for higher IVF success rates.
- Affordable IVF cost options with transparent pricing.
- Supportive team available throughout your entire journey.
Our mission is to provide not just treatment, but hope, compassion, and expert guidance every step of the way.
When to Consider IVF Treatment
IVF may be recommended when other fertility treatments have not been successful or in cases where specific medical conditions make natural conception difficult. You might consider IVF if:
- You have blocked or damaged fallopian tubes.
- Your partner has low sperm count or motility issues.
- You have endometriosis or other reproductive health conditions.
- You’ve experienced multiple unsuccessful attempts with IUI or other fertility treatments.
- You are of advanced maternal age and fertility is declining.
- You are part of an LGBTQ+ family or require donor eggs/sperm or surrogacy.
- You want to pursue fertility preservation before medical treatments that may affect fertility.
Precision IVF offers personalized guidance to help you understand if IVF is the right choice for your unique situation and ensures a supportive, expert-led journey toward parenthood.
IVF Pregnancy: What to Expect
Going through IVF can feel overwhelming but knowing what to expect can make the journey smoother. After the embryo transfer, your body begins the process of implantation. You may experience mild cramping, bloating, or hormonal changes. A pregnancy test is usually scheduled about 10–14 days after the transfer.
If the test is positive, your care continues with close monitoring, including blood tests and ultrasounds, to ensure the pregnancy is progressing well. Throughout the process, our team provides guidance, support, and answers to your questions, helping you feel informed and confident every step of the way.

Our IVF Process
At Precision IVF we provide patients with a personalized treatment plan that is designed to meet your individual needs and family-building goals. Our standard IVF treatment process includes the following steps:
1. Preparation for the Cycle
Patients receive birth control medication for a few weeks, generally less than a month to synchronize the growth of follicles.
2. Ovarian Stimulation
Ovarian stimulation involves taking hormone medications for approximately 8-14 days to stimulate multiple follicle development to increase the number of eggs retrieved. Patients are closely monitored by ultrasound and blood workups. Once follicle sizes and hormones reach appropriate levels, a “trigger shot” (HCG or Lupron) is administered to initiate the final egg maturation.
3. Egg Retrieval
The egg retrieval is scheduled approximately 35 hours after the trigger shot. This minor surgical procedure is performed under ultrasound guidance and has a guide to insert a thin needle through the wall of the vagina into the ovary to collect eggs from each follicle. This procedure may last 15 to 30 minutes and is usually done on an outpatient basis under sedation.
4. Sperm Processing
This is usually done on the day of the egg retrieval. Fresh or frozen sperm may be used and will be “washed” (or processed) using advanced laboratory techniques separating the sperm from the seminal fluid, increasing the number of motile sperm and improving the likelihood for fertilization. In instances when sperm collection on the day of egg retrieval looks stressful, semen sample can be collected ahead of time and cryopreserved in the andrology lab as a backup option. Some men with severe male factor infertility may require a testicular biopsy for extraction of sperm for IVF.
5. Egg Fertilization
Eggs are then fertilized either conventionally (by placing the egg and sperm in a dish to allow fertilization) or by injecting a single sperm directly into the egg (intracytoplasmic sperm injection or ICSI). ICSI is a micromanipulation procedure that allows fertilization even with very low sperm count.
A fertilization check is done approximately 18-19 hours after conventional insemination or ICSI. Fertilization is the union of male and female reproductive cells (sperm and egg) to produce a fertilized egg (zygote).
6. Embryo Development & Selection
The embryo(s) are then cultured to grow in the laboratory for 5-7 days. On the day of embryo transfer (done either on day 3 or day 5 for fresh embryo transfer) the embryo or blastocyst with the highest morphological grade is selected for transfer. Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) is performed at this time for patients who choose this testing. Remaining embryos can be cryopreserved for future transfer attempts.
7. Embryo Transfer
Embryo transfer requires the use of a small catheter to draw up the selected embryo(s) and to transfer them into the woman’s uterine cavity. This procedure is generally painless and usually does not require anesthesia. For best results we use ultrasound guidance for accurate catheter localization and transfer of the embryo into the uterine cavity. We follow the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) guidelines and typically transfer one or two embryos at a time, reducing the likelihood of multiple births. Upon completion of the transfer, the embryo(s) should “hatch” from their outer shell and implant into the uterine wall.
8. Next Steps
A blood test is performed typically nine to 11 days after transfer to determine if a woman is pregnant. If embryo implantation has occurred, the HCG hormone will be detected in the bloodstream and the woman will be considered pregnant. Patients who achieve pregnancy will schedule a follow-up visit for blood work and an ultrasound. For those patients who were not able to achieve pregnancy, we will schedule a consultation to review your cycle in detail and discuss further options to continue or alter the treatment.
Additional Services
Depending on your diagnosis and treatment plan, you may choose to include add-on services as a part of your IVF cycle. These can include:
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
- Facilitate fertilization or Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT).
- Assisted Hatching: This procedure is performed in order to help an embryo hatch out of its outer protective layering (zona pellucida) and implant into the uterus. In certain situations the outer shell surrounding the embryo is thickened and/or hardened, therefore not allowing it to “hatch,” or break out, and compromising an embryo’s ability to implant into the uterine wall. The procedure involves making a small incision into the outer shell just prior to the transfer of the embryo into the uterus. This may increase the likelihood that the embryo will implant into the uterine wall, resulting in a successful pregnancy.
- Cryopreservation and Embryo Freezing: During the IVF process, more embryos can develop than are used or transferred. In this case, there is the option to freeze (cryopreserve) any excess good quality embryos for future transfer attempts. Embryos are generally frozen at the blastocyst stage (five to seven days after fertilization). Vitrification is the newest technology in cryopreservation. This ultra-rapid freezing technique minimizes any ice crystal formation and potential damage to frozen embryo(s). Research studies have shown better post-thaw survival rates and higher live birth rates using embryo(s) frozen by this technique.
Micro/Mini IVF
Micro/Mini IVF is a very unique and simplified approach, reducing the cost, number of injections, and risk of hyperstimulation while maintaining good success rates. There are some studies that suggest Mini-IVF may be a better solution for low ovarian reserve and/or older patients.
Dr. Arya will work with you to determine if these options are right for you based on your needs and personal preferences.
FAQ's
1. How long does the IVF process take?
A complete IVF cycle typically takes 4–6 weeks, including consultation, ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization, and embryo transfer.
2. What is the success rate of IVF?
Success rates vary depending on age, medical history, and fertility factors. Our clinic strives to provide the highest possible success rates with personalized treatment plans.
3. How many IVF cycles are usually needed?
The number of cycles depends on individual fertility factors. Many patients achieve success within 1–3 cycles, while some may require additional attempts.
4.Are IVF treatments safe?
Yes, IVF is generally safe when performed under expert supervision. Our team monitors patients carefully to ensure safety and well-being throughout the process.

Begin Your Journey to Successful IVF
If you’ve been struggling to conceive, IVF may be the advanced and effective solution you’ve been looking for. At Precision IVF, we combine medical expertise with compassionate care to help you achieve your dream of parenthood.
Call us today or
schedule a consultation online to explore your IVF options. Together, we’ll create a personalized treatment plan designed to give you the best possible chance for a successful pregnancy.